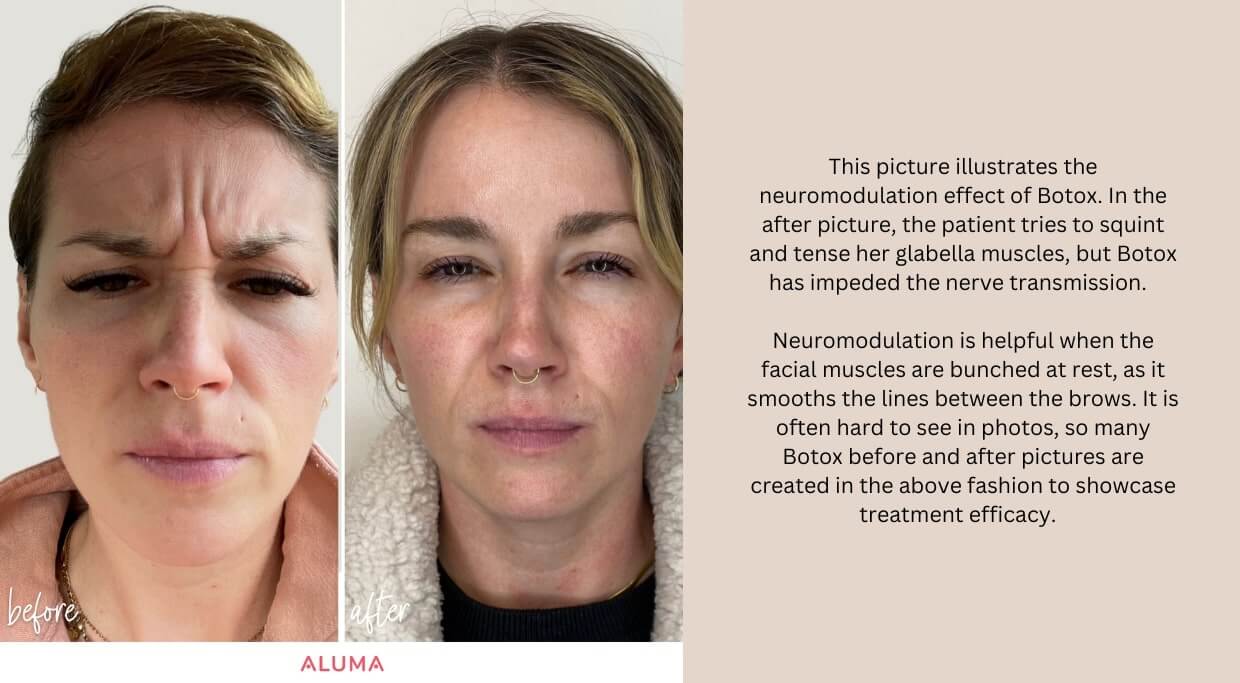
In the aesthetic world, Botox is an effective way to smooth lines and wrinkles caused by aging. Initially used for individuals with muscular hyperactivity disorders, Botox is now one of the most requested treatments for facial rejuvenation. Over 100 million vials have been sold in the United States alone since 2002. Botox is derived from Clostridium Botulinum, a spore-forming bacterium that produces the same neurotoxin known for botulism. Scientific research, proprietary formulations, and distribution standards have made Botox safe for medical applications. Botox arrives at clinics in a powder-filled vial packaged with dry ice to maintain effectiveness. Once ready for injection, Botox is reconstituted with bacteriostatic saline and refrigerated. An insulin syringe with a small diameter (31-gauge needle) is typically used for injection for treatment comfort. Classified as a neuromodulator, Botox impedes the neural signal to the muscles, modulating muscle contraction and smoothing the skin. Over time, wrinkles form due to repeated contractions of the facial musculature, squinting, raising the brows, and smiling. The muscles of expression become more robust and hold tension, often having difficulty returning to their “at-rest” state. This “push and pull” of the muscles versus the skin is like a game of tug of war where the muscles win and the skin bunches into a wrinkle. “Through the inhibition of neurotransmission between peripheral nerve endings and muscle fibers, botulinum toxin weakens or paralyzes skeletal muscle.” When the skeletal muscle is weakened, the skin can return to its original state, and the wrinkles are smoothed. The effects of Botox are transient; muscular function typically returns to baseline within a few months.
5 FDA-approved neuromodulators in the United States:
- Botox – OnabotulinumtoxinA – is a preservative-free, vacuum-dried powder that contains the Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin plus human albumin and sodium chloride. It is FDA-approved to smooth the lines between the eyes (glabellar region), the forehead lines, and the crow’s feet. Botox gained its FDA approval 20 years ago, the first on the market for cosmetic injections.
- Dysport – AbobotulinumtoxinA – is another botulinum toxin type A formulation that comes in a freeze-dried powder plus serum albumin and lactose. In 2009, Dysport gained FDA approval for glabellar lines, the lines between the eyebrows.
- Xeomin – IncobotulinumtoxinA – is a newer botulinum toxin type A formulation that comes in a freeze-dried powder plus human albumin and sucrose.
- Jeuveau – PrabotulinumtoxinA – was approved in 2019 for glabellar lines. It also comes in a freeze-dried powder.
- Daxxify -DaxibotulinumtoxinA – is the newest neuromodulator on the market. It was approved in 2022. It is the only FDA-approved (neuromodulator) to help smooth moderate to severe lines between the brows, lasting an average of six months.
Botox Duration
Typically, Botox lasts three months; however, the duration is site and dose-dependent, with larger doses lasting longer. In addition, clients that get repeated injections may notice their Botox lasting longer than three months due to musculature atrophy. After Botox injections, making facial expressions (smile, squint, raise brows) will assist in binding the neuromodulator to the injection site. Doing this 2-3 times within 6 hours of your Botox treatment is ample. Massaging the area should be avoided, especially above the brows. Botox takes effect around three days after treatment, with some muscles losing strength and tension before others. It is common to have slight asymmetry until the two-week marker when the neuromodulator peeks and most of the muscle fibers in the treatment area are calmed. Looking for a Botox treatment in Portland, OR? Visit Aluma Aesthetic Medicine for a comprehensive consultation and Botox treatment to smooth wrinkles and pump the brakes on aging.
References
- Botox Cosmetics
- Carruthers, Jean MD, FRCSC Overview of Botulism Toxin for Cosmetic Injections: Uptodate 2022.
- CDC.gov